Python basics
Overview
Teaching: 25 min
Exercises: 30 minQuestions
How do I assign values to variables?
How do I do arithmetic?
What is a built-in function?
How do I see results?
What data types are supported in Python?
Objectives
Create different cell types and show/hide output in Jupyter
Create variables and assign values to them
Check the type of a variable
Perform simple arithmetic operations
Specify parameters when using built-in functions
Get help for built-in functions and other aspects of Python
Define native data types in Python
Convert from one data type to another
Using the Jupyter environment
New cells
From the insert menu item you can insert a new cell anywhere in the notebook either above or below the current cell. You can also use the + button on the toolbar to insert a new cell below.
Change cell type
By default new cells are created as code cells. From the cell menu item you can change the type of a cell from code to markdown. Markdown is a markup language for formatting text, it has much of the power of HTML, but is specifically designed to be human-readable as well. You can use Markdown cells to insert formatted textual explanation and analysis into your notebook. For more information about Markdown, check out these resources:
- Jupyter Notebook Markdown Docs
- Markdown - a Visual Guide
- Mastering Markdown from Github
- Markdown official open source project
Hiding output
When you run cells of code the output is displayed immediately below the cell. In general this is convenient. The output is associated with the cell that produced it and remains a part of the notebook. So if you copy or move the notebook the output stays with the code.
However lots of output can make the notebook look cluttered and more difficult to move around. So there is an option available from the cell menu item to ‘toggle’ or ‘clear’ the output associated either with an individual cell or all cells in the notebook.
Creating variables and assigning values
Variables and Types
In Python variables are created when you first assign values to them.
a = 2
b = 3.142
All variables have a data type associated with them.
The data type is an indication of the type of data contained in a variable.
If you want to know the type of a variable you can use the built-in type() function.
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
s = "Hello World"
print(type(s))
<class 'int'>
<class 'float'>
<class 'str'>
There are many more data types available, a full list is available in the Python documentation. We will be looking a few of them later on.
Simple arithmetic operations
For now we will stick with the numeric types and do some arithmetic.
All of the usual arithmetic operators are available.
In the examples below we also introduce the Python comment symbol #.
Anything to the right of the # symbol is treated as a comment. To a large extent using Markdown cells in a notebook reduces the need for comments in the code, but occasionally they can be useful. - Don’t overdo them.
We also make use of the built-in print() function.
print("a =", a, "and b =" , b)
print(a + b) # addition
print(a * b) # multiplication
print(a - b) # subtraction
print(a / b) # division
print(b ** a) # exponentiation
print(2 * a % b) # modulus - returns the remainder
a = 2 and b = 3.142
5.1419999999999995
6.284
-1.142
0.6365372374283896
9.872164
0.8580000000000001
We need to use the print() function because by default only the last output from a cell is displayed in the output cell.
In our example above, we pass four different parameters to the first call of print(), each separated by a comma. A string "a = ", followed by the variable a, followed by the string "b = " and then the variable b.
The output is what you would probably have guessed at.
All of the other calls to print() are only passed a single parameter. Although it may look like 2 or 3, the expressions are evaluated first and it is only the single result which is seen as the parameter value and printed.
In the last expression a is multiplied by 2 and then the modulus of the result is taken. Had I wanted to calculate a % b and then multiply the result by two I could have done so by using brackets to make the order of calculation clear.
Arithmetic expressions can be arbitrarily complex, but remember people have to read and understand them as well.
Exercise
Create a new cell and paste into it the assignments to the variables a and b and the contents of the code cell above with all of the print statements. Remove all of the calls to the print function so you only have the expressions that were to be printed and run the code. What is returned?
Now remove all but the first line (with the 4 items in it) and run the cell again. How does this output differ from when we used the print function?
Practice assigning values to variables using as many different operators as you can think of.
Create some expressions to be evaluated using parentheses to enforce the order of mathematical operations that you require
Solution
- Only the last result is printed.
- The 4 ‘items’ are printed by the REPL, but not in the same way as the print statement. The items in quotes are treated as separate strings, for the variables a and b the values are printed. All four items are treated as a ‘tuple’ which are shown in parentheses, a tuple is another data type in Python that allows you to group things together and treat as a unit. We can tell that it is a tuple because of the
()A complete set of Python operators can be found in the official documentation . The documentation may appear a bit confusing as it initially talks about operators as functions whereas we generally use them as ‘in place’ operators. Section 10.3.1 provides a table which list all of the available operators, not all of which are relevant to basic arithmetic.
Using built-in functions
Python has a reasonable number of built-in functions. You can find a complete list in the official documentation.
Additional functions are provided by 3rd party packages which we will look at later on.
For any function, a common question to ask is: What parameters does this function take?
In order to answer this from Jupyter, you can type the function name and then type shift+tab and a pop-up window will provide you with various details about the function including the parameters.
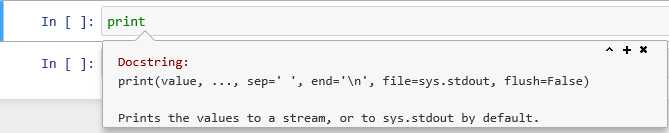
Exercise
For the
print()function find out what parameters can be providedSolution
Type ‘print’ into a code cell and then type
shift+tab. The following pop-up should appear.
Getting Help for Python
You can get help on any Python function by using the help function. It takes a single parameter of the function name for which you want the help
help(print)
Help on built-in function print in module builtins:
print(...)
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default.
Optional keyword arguments:
file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout.
sep: string inserted between values, default a space.
end: string appended after the last value, default a newline.
flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream.
There is a great deal of Python help and information as well as code examples available from the internet. One popular site is stackoverflow which specialises in providing programming help. They have dedicated forums not only for Python but also for many of the popular 3rd party Python packages. They also always provide code examples to illustrate answers to questions.
You can also get answers to your queries by simply inputting your question (or selected keywords) into any search engine.
A couple of things you may need to be wary of: There are currently 2 versions of Python in use, in most cases code examples will run in either but there are some exceptions. Secondly, some replies may assume a knowledge of Python beyond your own, making the answers difficult to follow. But for any given question there will be a whole range of suggested solutions so you can always move on to the next.
Data types and how Python uses them
Changing data types
The data type of a variable is assigned when you give a variable a value as we did above. If you re-assign the value of a variable, you can change the data type.
You can also explicitly change the type of a variable by casting it using an appropriate Python builtin function. In this example we have changed a string to a float.
a = "3.142"
print(type(a))
a = float(a)
print(type(a))
<class 'str'>
<class 'float'>
Although you can always change an integer to a float, if you change a float to an integer then you can lose part of the value of the variable and you won’t get an error message.
a = 3.142
print(type(a))
a = 3
print(type(a))
a = a*1.0
print(type(a))
a = int(a)
print(type(a))
a = 3.142
a = int(a)
print(type(a))
print(a)
<class 'float'>
<class 'int'>
<class 'float'>
<class 'int'>
<class 'int'>
3
In some circumstances explicitly converting a data type makes no sense; you cannot change a string with alphabetic characters into a number.
b = "Hello World"
print(type(b))
b = int(b)
print(type(b))
<class 'str'>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-8-9f5f81a470f9> in <module>()
2 print(type(b))
3
----> 4 b = int(b)
5 print(type(b))
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'Hello World'
Strings
A string is a simple data type which holds a sequence of characters.
Strings are placed in quotes when they are being assigned, but the quotes don’t count as part of the string value.
If you need to use quotes as part of your string you can arbitrarily use either single of double quotes to indicate the start and end of the string.
mystring = "Hello World"
print(mystring)
name = "Peter"
mystring = 'Hello ' + name + ' How are you?'
print(mystring)
name = "Peter"
mystring = 'Hello this is ' + name + "'s code"
print(mystring)
Hello World
Hello Peter How are you?
Hello this is Peter's code
String functions
There are a variety of Python functions available for use with strings. In Python a string is an object. An object put simply is something which has data, in the case of our string it is the contents of the string and methods. methods is another way of saying functions.
Although methods and functions are very similar in practice, there is a difference in the way you call them.
One typical bit of information you might want to know about a string is its length for this we use the len() function. For almost anything else you might want to do with strings, there is a method.
mystring = "Hello World"
print(len(mystring))
11
If you want to see a list of all of the available methods for a string (or any other object) you can use the dir() function.
print(dir(mystring))
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
The methods that you can use are those that do NOT start with ‘__’.
Some examples of the methods are given below. We will use others when we start reading files.
myString = "The quick brown fox"
print(myString.startswith("The"))
print(myString.find("The")) # notice that string positions start with 0 like all indexing in Python
print(myString.upper()) # The contents of myString is not changed, if you wanted an uppercase version
print(myString) # you would have to assign it to a new variable
# The methods starting with 'is...' return a boolean value of either True or False
print(myString.isalpha())
# the example above returns False because the space character is not considered to be an Alphanumeric value.
# In the example below, we can use the replace() method to remove the spaces and then check to see if the result 'isalpha'
# chaining method in this way is quite common. The actions take place in a left to right manner. You can always avoid using chaining by
# using intermediary variables.
print(myString.replace(" ","").isalpha())
True
0
THE QUICK BROWN FOX
The quick brown fox
False
True
If you need to refer to a specific element (character ) in a string, you can do so by specifying the index of the character in ‘[]’ you can also use indexing to select a substring of the string.
myString = "The quick brown fox"
print(myString[0])
print(myString[12])
print(myString[18])
print(myString[0:3])
print(myString[0:]) # from index 0 to the end
print(myString[:9]) # from the beginning to one before index 9
print(myString[:9])
T
o
x
The
The quick brown fox
The quick
The quick
Basic Python data types
So far we have seen three basic Python data types; Integer, Float and String. There is another basic data type; Boolean. Boolean variables can only have the values of either True or False. (Remember, Python is case sensitive, so be careful of your spelling.)
We can define variables to be of type boolean by setting their value accordingly.
bool_val_t = True
print(type(bool_val_t))
print(bool_val_t)
bool_val_f = False
print(type(bool_val_f))
print(bool_val_f)
We can also get variables of this type using comparison operators, which you might have found in the exploratory exercise earlier
bool_val = True
if bool_val :
print("bool_val is",bool_val)
bool_val = False
if bool_val :
print("bool_val is",bool_val)
bool_val is True
Exercise
Can you predict what will be returned from the following code segments
bool_val1 = 'TRUE' if bool_val1 : print("bool_val1 is",bool_val1) bool_val2 = 'FALSE' if bool_val2 : print("bool_val2 is",bool_val2) bool_val3 = 1 if bool_val3: print("bool_val3 is",bool_val3)
Exercise
Try to predict what will print for each of the following. Then run the code and summarize your findings about what how to represent boolean values and how other values cast to boolean type in either a markdown cell or a comment
bool_val1 = 'TRUE' print(type(bool_val1)) print(bool(bool_val1)) bool_val2 = 'FALSE' print(bool(bool_val2)) bool_val3 = 1 print(bool(bool_val3)) bool_val4 = 0 print(bool(bool_val4)) bool_val5 = -1 print(bool(bool_val5)) bool_val6 = -1 print(bool(bool_val6))Solution
0 is represented as False and everything else, whether a number or string is counted as True
Structured data types
A structured data type is a data type which is made up of some combination of the base data types in a well defined but potentially arbitrarily complex way.
The list
A list is a set of values, of any type separated by commas and delimited by ‘[’ and ‘]’
list1 = [6, 54, 89 ]
print(list1)
print(type(list1))
list2 = [3.142, 2.71828, 9.8 ]
print(list2)
print(type(list2))
myname = "Peter"
list3 = ["Hello", 'to', myname ]
print(list3)
myname = "Fred"
print(list3)
print(type(list3))
list4 = [6, 5.4, "numbers", True ]
print(list4)
print(type(list4))
[6, 54, 89]
<class 'list'>
[3.142, 2.71828, 9.8]
<class 'list'>
['Hello', 'to', 'Peter']
['Hello', 'to', 'Peter']
<class 'list'>
[6, 5.4, 'numbers', True]
<class 'list'>
The range function
In addition to explicitly creating lists as we have above it is very common to create and populate them automatically using the range() function in combination with the list() function
list5 = list(range(5))
print(list5)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Unless told not to range() returns a sequence which starts at 0, counts up by 1 and ends 1 before the value of the provided parameter.
This can be a cause of confusion. range(5) above does indeed have 5 values, but rather than being 1,2,3,4,5 which you might naturally think, they are in fact 0,1,2,3,4. The range starts at 0 and stops one before the value of the single parameter we specified.
If you want different sequences, then you can modify the behavior of the range() function by using additional parameters.
list6 = list(range(1, 9))
print(list6)
list7 = list(range(2, 11, 2))
print(list7)
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
When you specify 3 parameters as we have for list(7); the first is start value, the second is one past the last value and the 3rd parameter is a step value by which to count. The step value can be negative
list7 produces the even numbers from 1 to 10.
Exercise
- What is produced if you change the step value in
list7to -2 ? Is this what you expected?- Create a list using the
range()function which contains the even number between 1 and 10 in reverse order ([10,8,6,4,2])Solution
list7 = list(range(2, 11, -2)) print(list7) list8 = list(range(10, 1, -2)) print(list8)
The other main structured data type is the Dictionary. We will introduce this in a later episode when we look at JSON.
Key Points
The Jupyter environment can be used to write code segments and display results
Data types in Python are implicit based on variable values
Basic data types are Integer, Float, String and Boolean
Lists and Dictionaries are structured data types
Arithmetic uses standard arithmetic operators, precedence can be changed using brackets
Help is available for builtin functions using the
help()function further help and code examples are available onlineIn Jupyter you can get help on function parameters using shift+tab
Many functions are in fact methods associated with specific object types